Space Exploration
Merit Badge





Space Exploration Merit Badge Supplementals
(created Wed. July 15, 2015 - the day after New Horizons visited Pluto)
(updated Mon. Sep. 26, 2016)
The Space Exploration merit badge is detailed at:
http://meritbadge.org/wiki/index.php/Space_Exploration
which shares:
“Space is mysterious. We explore space for many reasons, not least because we don't know what is out there, it is vast, and humans are full of curiosity. Each time we send explorers into space, we learn something we didn't know before. We discover a little more of what is there.”
In addition to these insights about “why should we explore space?”...
... “Scouting and Space Exploration” / http://www.scouting.org/About/FactSheets/scouting_space.aspx shares:
“The BSA launched the Space Exploration merit badge in 1965.
-
■Since then, over 420,000 badges have been earned by Scouts.
-
■The requirements for earning this badge may include:
-
■building, launching, and recovering a model rocket
-
■designing an earth-orbiting space station
-
■learning how satellites stay in orbit
-
■and more…(See www.scouting.org for exact requirements.)
-
NASA provides students, particularly Scouts, with many opportunities.
-
■Ideas and information for Cub Scout achievements can be found at: http://spaceplace.jpl.nasa.gov/en/kids/cubscouts
-
■Ideas and information for Boy Scout achievements can be found at:
-
■http://genesismission.jpl.nasa.gov/product/community/scout_overview.html
The National Aeronautic and Space Administration selected the first group of
astronauts in 1959.
-
■Of the 320 pilots and scientists selected since 1959, 181 were in Scouting.
-
■Of the 12 men to walk on the moon, 11 were Scouts.”
“Scouting and Space Exploration” / http://www.scouting.org/About/FactSheets/scouting_space.aspx
also lists each Scout Astronaut, providing rank and NASA mission.
Space Exploration, the two-part definition:
Space
Definition of space
noun, often attributive \ˈspās\
5 : the region beyond the earth's atmosphere or beyond the solar system
source: http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/space
which could also be understood to be defined as: “beyond the earth’s atmosphere...”
Space is generally recognized to begin at 100 kilometers / 62 miles, above sea level.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Outer_space
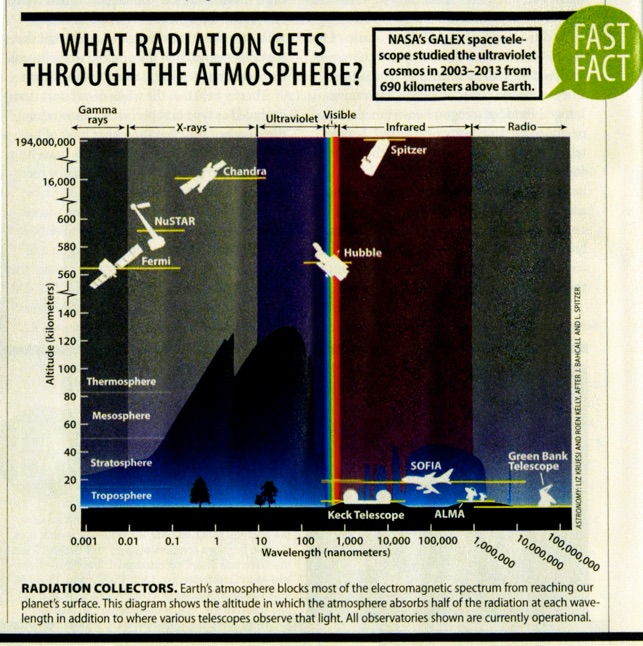
While this graphic, from the June, 2014 issue of Astronomy Magazine provides insights into relative altitudes of our atmosphere and how much solar radiation gets through each layer, it also shows the layers of the earth’s atmosphere, which helps us understand “where space begins...” 100Km / 62 m is in the Thermosphere.
Exploration
noun ex·plo·ra·tion \ˌek-splə-ˈrā-shən, -ˌsplȯ-\
: the act or an instance of exploring
source: http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/exploration
which leads to...
Explore
verb ex·plore \ik-ˈsplȯr\
transitive verb
1 a : to investigate, study, or analyze : look into <explore the relationship between social class and learning ability> —sometimes used with indirect questions <to explore where ethical issues arise — R. T. Blackburn>
b : to become familiar with by testing or experimenting <explore new cuisines>
2 : to travel over (new territory) for adventure or discovery
3 : to examine especially for diagnostic purposes <explore the wound>
intransitive verb
: to make or conduct a systematic search <explore for oil>
source: http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/exploring
For comparison, for reference...
How are astronomy (two awesome Merit Badges) similar, but different?
Astronomy is the “studying of the heavens... from earth” (which can use space-based telescopes).
Space Exploration is the “going to the heavens,” departing earth, and going there... either in person, or via space probes.
MeritBadge.org’s Space Exploration page also contains a Space Exploration Merit Badge worksheet to write your answers to the requirements.
Scouting.org’s Merit Badge page also includes digital copies of the requirements from the paper merit badge books.
The Space Exploration requirements are available at: Space Exploration Current.
The purpose of this page is to 1) list the Space Exploration merit badge requirements and 2) provide information about the answers beyond those provided in the Merit Badge book; please know that only those answers in the book are required to complete the merit badge. The information on this page is shared to provide additional insights into the requirement and to encourage enthusiasm about all that is exciting about the exploring the universe beyond our planet, in person and through unmanned spacecraft.
Many of the resources are links, and I also share some resources I scanned from Astronomy Magazine - http://www.astronomy.com, a publication of Kalmbach Publishing Co., of Milwaukee, WI - http://kalmbach.com. While Astronomy magazine is focused on that discipline, which supports that Merit Badge, it does share much about Space Exploration, as the two disciplines are quite related. So please do not let the magazine’s name cause confusion, as it does provide articles about both Merit Badges.
Space Exploration requirements are bolded.
1. Tell the purpose of space exploration and include the following:
a. Historical reasons
b. Immediate goals in terms of specific knowledge
c. Benefits related to Earth resources, technology, and new products.
d. International relations and cooperation
Your Merit Badge book/manual has great information to help answer these questions.
As you read it, you may also have the following questions.
What are the different ways to explore space?
Answer:
-
-Manned
-
-Unmanned
What are the pros and cons of each of the ways to explore space?
There are several reasons... to discuss with your Merit Badge Counselor.
What countries have:
-
-A Space program?
-
-Have astronauts?
-
-Have astronauts who have flown in space?
-
-Were those astronauts launched by their own rockets, or the rockets of another country’s space program?
-
-Launched rockets into space?
-
-People into space?
?
You can find the answers at:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_government_space_agencies
What was the first satellite, the first spacecraft,
when was it launched (year),
and what nation launched it?
One helpful resource is:
http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/S/Sputnik.html
What was the United States’ first satellite, the first spacecraft,
when was it launched (year),
and what did it discover?
One helpful resource is:
http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/E/Explorer.html
What was the first person in space,
from what country,
in what year did he first orbit,
and what does that country call their astronauts?
One helpful resource is:
http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/sts1/gagarin_anniversary.html
What was the United States’ first man in space,
and in what year did he first orbit (and what did he do first on the moon?)?
Helpful resource include:
http://www.nasa.gov/multimedia/imagegallery/image_feature_171.html
&
http://www.space.com/17385-alan-shepard-first-american-in-space.html
(sub-orbital)
&
http://www.space.com/17263-john-glenn-astronaut-biography.html
Who was the first woman in space, and when did she first fly?
Helpful resource include:
http://www.space.com/21571-valentina-tereshkova.html
Who was the first American woman in space, and when did she first fly?
Helpful resource include:
http://www.nasa.gov/multimedia/imagegallery/image_feature_2533.html
While this is focused on the Boy Scout Merit Badge, how many of America’s women / female astronauts have been Girl Scouts?
Helpful resource include:
http://spaceflightsystems.grc.nasa.gov/girlscouts/gsusa_astro.html
What countries have landed spacecraft on other planets and/or planets’ moons?
One helpful resource is:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_landings_on_extraterrestrial_bodies
Extraterrestrial / E.T. definition
adjective ex·tra·ter·res·tri·al \-tə-ˈres-trē-əl, -ˈres(h)-chəl\
: originating, existing, or occurring outside the earth or its atmosphere <extraterrestrial life>
source: http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/extraterrestrial
What country is the only country to have landed man on our moon?
hint:

image source: http://usflag.org/history/the50starflag.html
Of the American astronauts who visited the moon (in the Apollo program), how many walked on the moon, and how many remained in lunar orbit?
Helpful resources to determine the answer include:
http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/apollo/index.html
&
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/lunar/apollo.html
What was a key tool (think... really big rocket) that got us to the moon?
Helpful resources to determine the answer include:
http://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/5-8/features/nasa-knows/what-was-the-saturn-v-58.html
&
http://www.space.com/18422-apollo-saturn-v-moon-rocket-nasa-infographic.html
Of the American astronauts who walked on the moon, and performed their mission there (they weren’t just there for a stroll), how many were Scouts?
Answer:
- “Of the 12 men to walk on the moon, 11 were Scouts.”
source: http://www.scouting.org/About/FactSheets/scouting_space.aspx
What are some of the many missions flown by the nations/countries with space programs?
Helpful resources to determine the answer include:
http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/S/spacecraft_list.html
Are national space programs the only way to get into space today?
-
-Yes
or -
-No
?
What is the X-Prize / XPRIZE, ...
The X-Prize is the award from the same-named organization, that encourages small teams to achieve “bold and audacious” goals.
... what is its association with St. Louis, ...
The first X-Prize is/was the Ansari XPRIZE, which
“Funded by the Ansari family, the Ansari XPRIZE challenged teams from around the world to build a reliable, reusable, privately financed, manned spaceship capable of carrying three people to 100 kilometers above the Earth's surface twice within two weeks.
The prize was awarded in 2004 and along with it, a brand new private space industry was launched.”
St. Louis link: this was the first X-Prize, inspired in St. Louis in 2001 by the St. Louis group in the 1920s who created the $25,000 prize that Charles Lindbergh won in his first-ever solo non-stop flight across the Atlantic.
Burt Rutan and the Scaled Composites team won, with their SpaceShipOne:
http://www.scaled.com/projects/tierone/
... and why is it mentioned here?
While initially focused on the Ansari XPRIZE’s goal of a reusable space vehicle, it has expanded beyond space exploration BUT
there are still two Space Exploration-related XPRIZES to be won:
-
-http://lunar.xprize.org
“A $30 MILLION COMPETITION
TO LAND A PRIVATELY FUNDED
ROBOT ON THE MOON
The Google Lunar XPRIZE incentivizes space entrepreneurs to create a new era of affordable access to the Moon and beyond.” -
-http://lunarlander.xprize.org
“A $2M COMPETITION TO ADVANCE REPEATED ROCKET TRAVEL TO THE MOON.
As part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program the Northrop Grumman Lunar Lander XCHALLENGE not only jumpstarted a new era of sustainable lunar exploration, it demonstrated the power of partnership. When government, space agencies and entrepreneurs work together, amazing things can be accomplished, sometimes at a fraction of the cost. On November 5, 2009, XPRIZE and NASA announced the winners in an awards ceremony in Washington D.C.”
What are some of the current companies working to launch space missions?
Helpful resources to determine the answer include:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_private_spaceflight_companies

SpaceX

Orbital ATK:

Blue Origin

Virgin Galactic
What is just one of many good sources of launch information?
Spaceflight Insider - http://www.spaceflightinsider.com
This page continues on: Space Exploration, Part 2




These are all of the links to the Astronomy Merit Badge pages:
Astronomy Merit Badge - Extra “Fun Facts”
Astronomy - Great American Eclipse
Astronomy - Great American Eclipse 2017


These are all of the links to the Space Exploration Merit Badge pages:
New Horizons - Mission Overview
New Horizons - Pluto Resources


All images were scanned directly from the magazine using the Halo Scanner Mouse - http://shop.halo2cloud.com/collections/computer-and-backup/products/scanner-mouse, which I received as a Christmas present from my mother in 2013.



Regardless your desire to pursue a career in space exploration, it is hoped that you learned enough about exploring space through this merit badge to at least be interested to continuously look up at the sky in awe and wonder, and think about what you may want to explore if you were to go “out there” or were to send a probe “out there.”
If you pursue with enthusiastic interest, that’s great. If you do make a career in the field, GREAT.
May all be better off having completed your Space Exploration Merit Badge than you were before you started.









